| Price | 13000-80000 USD |
| Delivery Time | 20-25 days |
| Available | In Stock |
| Package | In Free Fumigation Wood Box |
| Guarantee | 1 Year |
| Shipping | By Sea or By Air |
| Payment Method | Wire Transfer or Western Union |
| Brand | Victor |
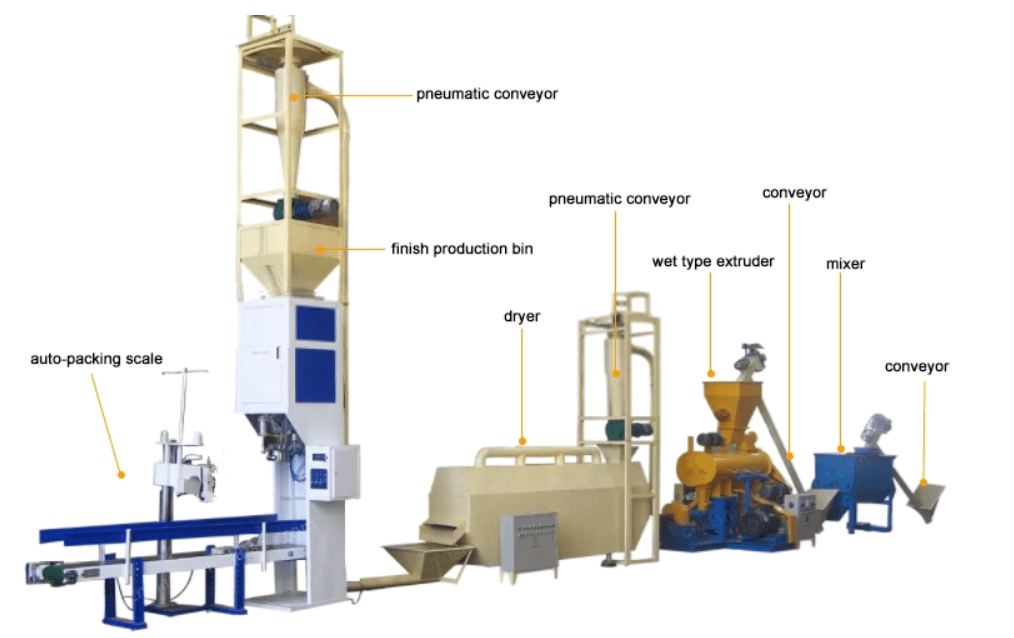
Floating Fish Feed Production Line Overview
| Production Output | 0.5-5 t/h |
| Power | Electric motor |
| Voltage | 110-415V |
| Raw Materials | Cereal, corn, wheat, barley flour, soybean, fish meal, bone powder, etc |
| Type | dry type and wet type |
| Final Pellet Size | 0.9-10 mm |
| Application | producing floating pellets |
| Used For | shrimp, catfish, tilapia, fish, and other aquatic feed |
floating fish feed production line video
Understanding Floating Feed Manufacturing Systems
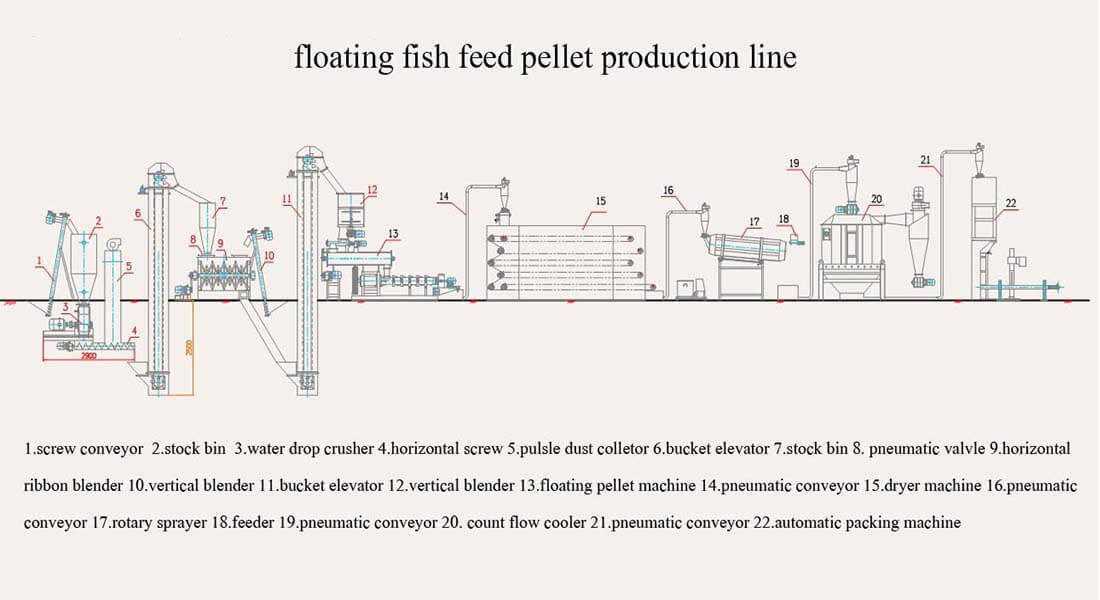
floating fish feed production line is a full automatic line for aquatic farmers to make floating fish feed. It makes aquatic food pellets that float on water. The production plant includes a crusher, mixer, dryer, and extruder.
you can use corn, soybean, wheat, and fish meals as the raw materials. The floating fish feed processing plant can turn them into healthier aquatic food bits. These floating pellets can different shapes and tastes. They work for goldfish, catfish, shrimp, and turtles.
the floating fish feed processing line can make 100kg to 5000 kg per hour. it is best for big aquatic farming and aquatic food factories. This floating fish feed production line can also make dog and cat food pellets. All parts can use 304 stainless steel to keep the feed clean and safe.

Key Machinery Components for Fish Feed Manufacturing
crusher machine
First, you need to crush raw materials into fine powder with a fish feed crusher. this step is very important to create aquatic food that floats well on water.
The crusher breaks corn, wheat, and other ingredients into perfect small pieces. These crushed bits need to be just the right size – not too big, not too small. correct size makes sure aquatic can eat and digest the food easily.
when crushing, you have to control how fine the powder is crushed. Different aquatic food pellet need different sizes. Always follow the size guide for the best floating aquatic food.
Requirement of Powder Raw Materials
| die size (mm) | powder fineness required |
| 1.0 | 95% at 90-100 mesh |
| 1.5 | 95% at 80 mesh |
| 2.0 | 95% at 80 mesh |
| 3.0 | 95% at60 mesh |
| 4.0 | 95% at 60 mesh |
| 5.0 | 95% at 60 mesh |
mixer machine
A fish feed mixer is important when you use different raw materials. It can make sure fully mixing with nutrient and food quality.
extruder machine
the extruder machine is the main equipment in floating fish feed production line. it turns powder materials into pellets.
dryer machine
pellet dryers are important because wet pellets will cause problems. When making aquatic food, you have to add 25%-30% water in the raw materials. If you don’t dry the pellets, they will get sticky and soft.
Wet pellets stick together in bags and get moldy. This makes them hard to store or ship. This dryer is used to remov extra moisture. Dry pellets can stay longer time.
cooler machine
Even when aquatic food pellets look dry, they still need cooling. because even steam dries the pellets, it takes out water but leaves them very hot. If you pack them while still warm, hidden moisture can form again. The cooler machine is an air counter-flow cooler for hot pellets.
It brings their heat down to safe levels. if not cooling, the leftover temperature will generate moisture inside storage bags. This moisture can grow mold and ruin the food. Farmers using coolers report 30% less spoiled food each month.
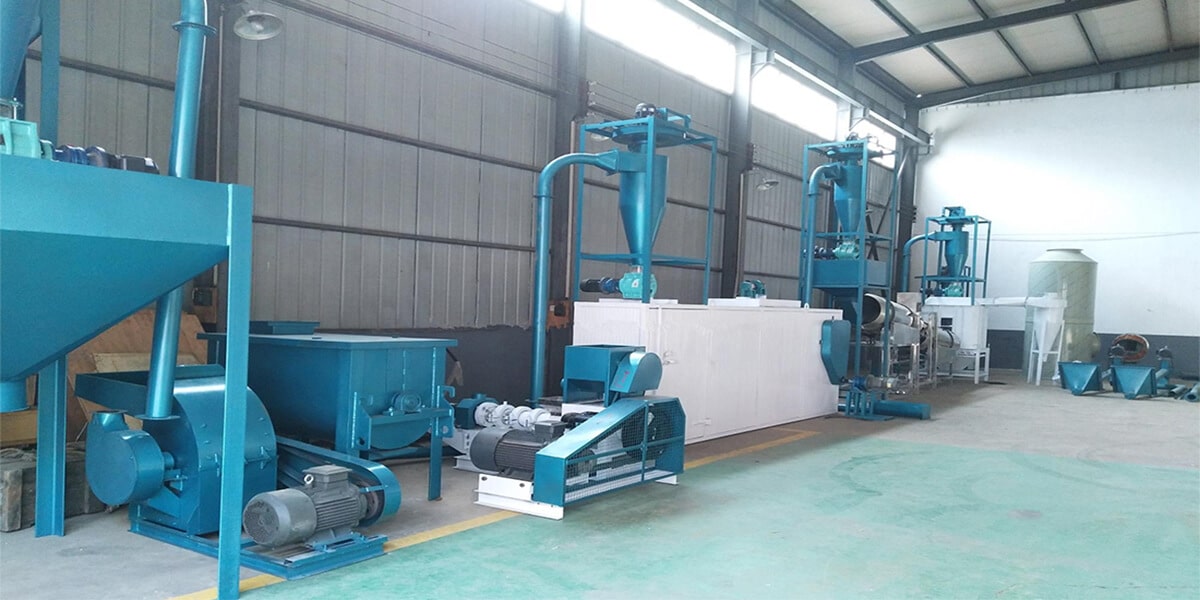

Step-by-Step Floating Feed Manufacturing Process
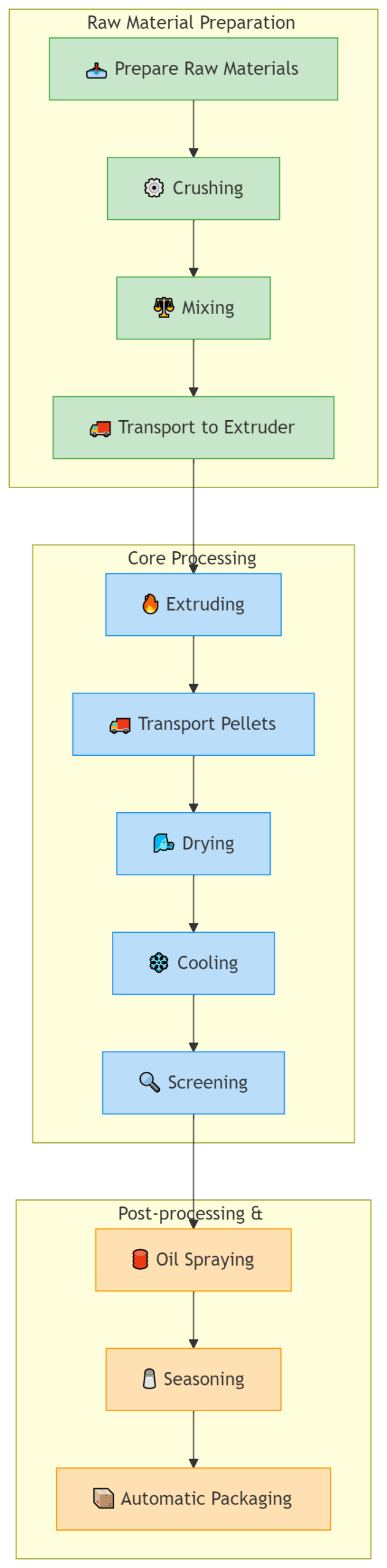
floating fish feed production line with PLC Control & Energy Saving
the floating fish feed production plant uses advanced technology to make a lot of aquatic food but using less power. Its parts work together like building blocks, so the floating fish feed produciton line is easy to ship and set up.
A computer brain (PLC) runs the whole system which save 30% energy. It has warning lights that flash if something’s wrong. Workers can control everything with simple buttons.
you can change the die to make different pellet sizes. The floating fish feed production line makes the food fast at high temperature to keep nutrients safe. it makes proteins and starches easier to digest, so aquatic animals will eat more.
high pressure ensures top quality feed and making speed. Electric heaters help to puff up the food like popcorn, it make the food floating better.
Essential Raw materials for Floating Fish Feed
Fish meal
The feed gets its protein from two smart sources: 1. leftover fish from we eat. they save the heads and bones to make aquatic food. 2. special fish like herring and menhaden. These small fish are nutrient-rich. Farmers mixing both sources report 15% faster growth.
Shrimp mix
These tiny creatures give aquatic two good stuffs: 1. strong muscles from protein. 2. bright colors from natural vitamins. the farmers who use shrimp meal see 18% brighter colors in their stock.
Squid meal
Squid meal comes from the soft organs of squid left over after canning. This gives young fish easy-to-digest protein for healthy growth. it is rich with amino acids, vitamins, and minerals. The natural 1-1.5% cholesterol helps baby fish develop strong bodies.
it can help fish to digest easily. The shrimp’s algae diet means they also carry plant nutrients. aquatic farming using brine shrimp report 25% faster growth and healthier-looking aquatic.
Spirulina
Spirulina is a natural superfood from water. This powder is rich with natural protein and vitamins like A, C, and B vitamins. It contains color-boosting nutrients and minerals fish need. the aquatic farmers who use spirulina report 30% brighter colors and stronger aquatic.
Grain Meal
Wheat gives goldfish and koi the fiber they need for healthy digestion. it is rich with vitamin E that helps aquatic to grow helathier and look colorful.
Soybean meal is a plant-based protein powerhouse. Many aquatic farmer now use it instead of fish-based feeds. This can help baby fish develop strong muscles and saves ocean resources.